💡Design Thinking Demystified: A Practical Introduction for Professionals

In today's fast-paced business world, 'innovation' is a word thrown around constantly. But what does it actually mean, and more importantly, how can professionals like you and me actually do it?
Innovation is the processes through which an idea turns into an invention, and that invention fundamentally changes the way people go about their activity, be it in their personal or professional life. A common misunderstanding is that people don't do innovation, but they aspire to introduce an innovative solution to the world that, if widely adopted, can be coined as an innovation or a trully innovative product.
There are many ways of going about innovation, but today I wanted to talk about one approach which is starting to be widely used for it's guaranteed success: Design Thinking. So buckle down for 5 minutes and let's learn a little about what this process entitles.
What is Design Thinking (DT)?

[Design Thinking is] a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer's toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success. - David Kelley, 1999 (IDEO)
Simply put, Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving and innovation. It’s about deeply understanding people's needs and creating solutions that truly resonate with the end user. It's a practical, iterative process for tackling complex problems by putting people at the heart of the solution and integrating their insight throughout the process.
DT isn't new : before David Kelley coined the term in 1999, many companies had already adopted human-centered design into their innovation frameworks. As a matter of fact, the Institute for Human Centered Design (IHCD) was founded in 1978 by Elaine Ostroff and Cora Beth Able, an outgrowth of the Arts and Human Services Project, a multi-disciplinary graduate program supported by the Massachusetts Department of Mental Health at the Massachusetts College of Art in Boston. This was way before David saw this approach as a fundamental tool for innovation accross all domains.
Why is Design Thinking Relevant to Professionals?

Pain Points Adressed
Professionals across industries often grapple with stagnant innovation, leading to a sense of being outpaced by competitors. The advantage of the Design Thinking approach is that it offers a framework to break free from this rut by emphasizing user-centered problem-solving.
It tackles the challenge of a lack of customer understanding by
- fostering empathy and deep insights,
- ensuring solutions directly address real needs.
Inefficient problem-solving, characterized by endless meetings and unfocused brainstorming, is streamlined through Design Thinking's iterative process, leading to quicker and more effective results.
Ultimately, it helps professionals develop solutions that resonate, avoiding costly misses and fostering genuine customer engagement.
Benefits
Design Thinking offers numerous benefits, namely it :
- empowers professionals to develop truly innovative solutions by shifting the focus from internal assumptions to user-centric insights, leading to products and services that resonate deeply.
- significantly reduces the risk of developing solutions that miss the mark by rigorously testing prototypes and iterating based on real-world feedback, saving time and resources.
- enhances collaboration and communication within teams by providing a shared framework for problem-solving, fostering a culture of creativity and shared understanding.
- accelerates the problem-solving process by providing a structured and iterative approach, enabling professionals to move from ideation to implementation with greater efficiency and confidence.
It's important to note that Design Thinking is a philosophy of how to go about innovation and not strict guidelines. Innovation by nature is a chaotic process, but DT helps channel the energy when practitioners may feel lost in the process.
A Glimpse into the Design Thinking Process
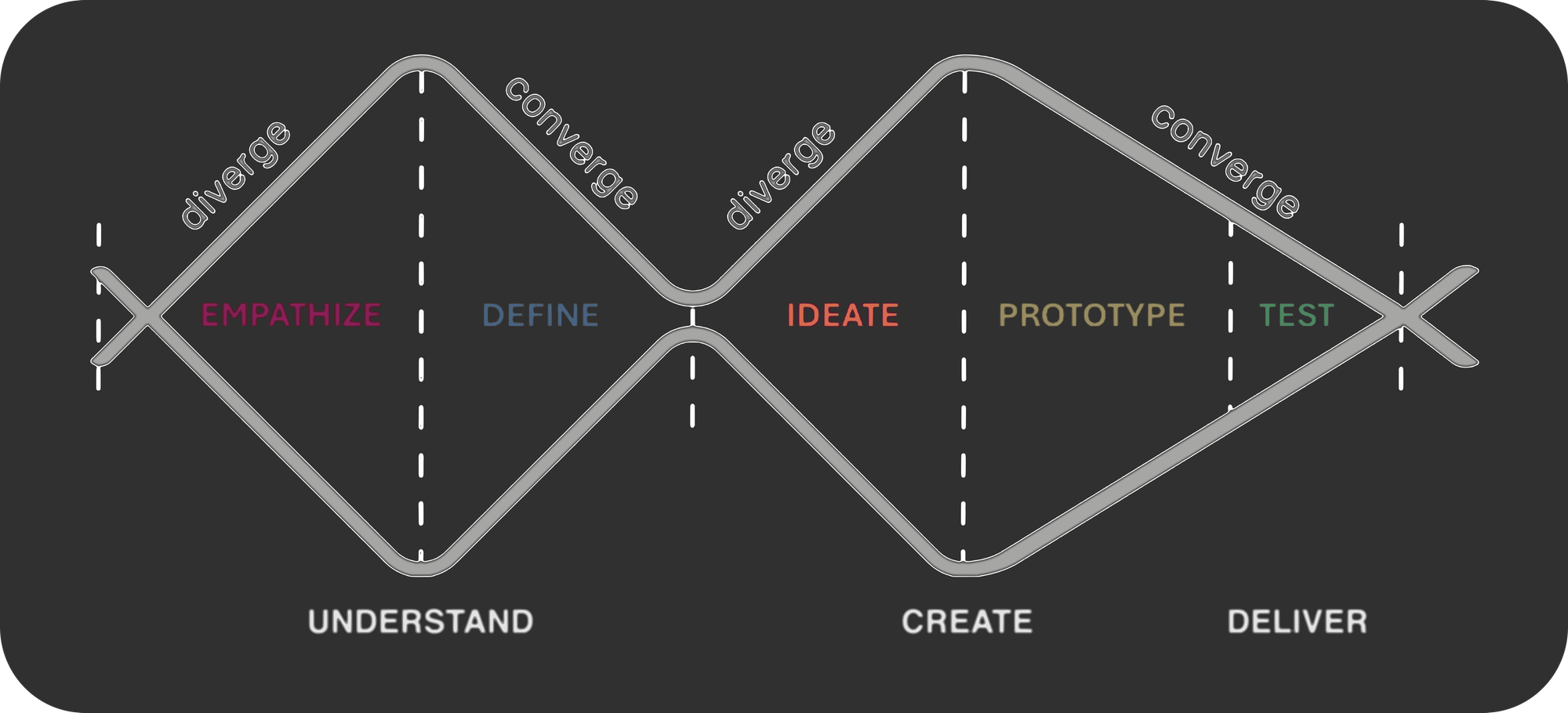
Design Thinking is lead using 5 phases :
- Empathize - Conduct Interviews, Uncover Emotions, Seek Stories
- Define - Reframe and Create Human-Centric Problem Statements, Identify Meaningful Surprises and Tensions, Infer Insights
- Ideate - Brainstorm Radical Ideas, Build on Others' Ideas, Suspend Judgement
- Prototype - Create Low-Res Objects and Experiences, Role Play to Understand Context and Key Features, Quickly Build to Think and Learn
- and Test - Test with Customers to Refine Solutions and Gather Ideas, Gain Deeper Empathy, Embrace Failure
Each step of the process incorporates different tools and frameworks to converge and diverge thoughts with the goal of exhaustively navigating the problem space and solution space of a given initial pain point. Although the diagram may seem like a linear process, it is in fact highly interative and practitioners don't hesitate to go back to previous steps if they gain insight that might add to the reflection.
Practical First Steps for Professionals

- Start by Asking 'Why?' More Often: Whenever you encounter a problem, resist jumping to solutions. Instead, practice asking 'Why?' repeatedly to dig deeper and uncover the root cause.
- Talk to Your Users (or Customers): Make a conscious effort to gather direct feedback from the people you are designing for. Even informal conversations can provide invaluable insights.
- Embrace 'Brainstorming' (Done Right): Facilitate a brainstorming session with your team, focusing on quantity over quality initially, and encouraging wild ideas.
- Create a Simple Prototype: For your next project, even a small one, try creating a quick sketch or mockup to visualize your idea before jumping into full development.
Recap
To sum up, Design Thinking emerges as a powerful and practical approach to innovation for professionals seeking to thrive in today's dynamic business landscape. By emphasizing a human-centered methodology, Design Thinking offers a structured yet flexible framework to move beyond stagnant practices, foster a deep understanding of user needs, and streamline problem-solving efforts.
Professionals can benefit from Design Thinking by developing truly innovative and resonant solutions, mitigating risks associated with misguided developments, enhancing team collaboration, and accelerating the entire problem-solving process. Embracing the iterative five-phase process and incorporating simple first steps like asking 'Why?', engaging with users, and prototyping ideas can empower any professional to unlock their innovative potential and achieve meaningful results in their respective fields.
What are your experiences with Design Thinking? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
In future articles, we'll dive deeper into each stage of the Design Thinking process. Stay tuned!
